

This means that the user’s identity is better protected when browsing onion services compared to traditional websites. In this case, there is no cleartext request from the exit node with the resulting metadata to the target server. Unlike traditional websites, access to onion services is completely encrypted via the Tor Browser. The user must know the exact address of the service in order to access it directly. onion and are not indexed by search providers such as Google. These web services use the Top Level Domain (TLD). Onion services refer to web content intended specifically for the use by the Tor network. has been responsible for the open source project. Since 2006, the non-profit organization The Tor Project, Inc. The Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) also participated in the development of Tor. government agencies, initially by the United States Naval Research Laboratory with the support of the Office of Naval Research (ONR) and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA). In the early years, the project was largely driven and developed by U.S. The concept and development of the technology date back to the year 2000. It has now become more common to capitalize only the first letter – “Tor” – which is also how the developers refer to it.
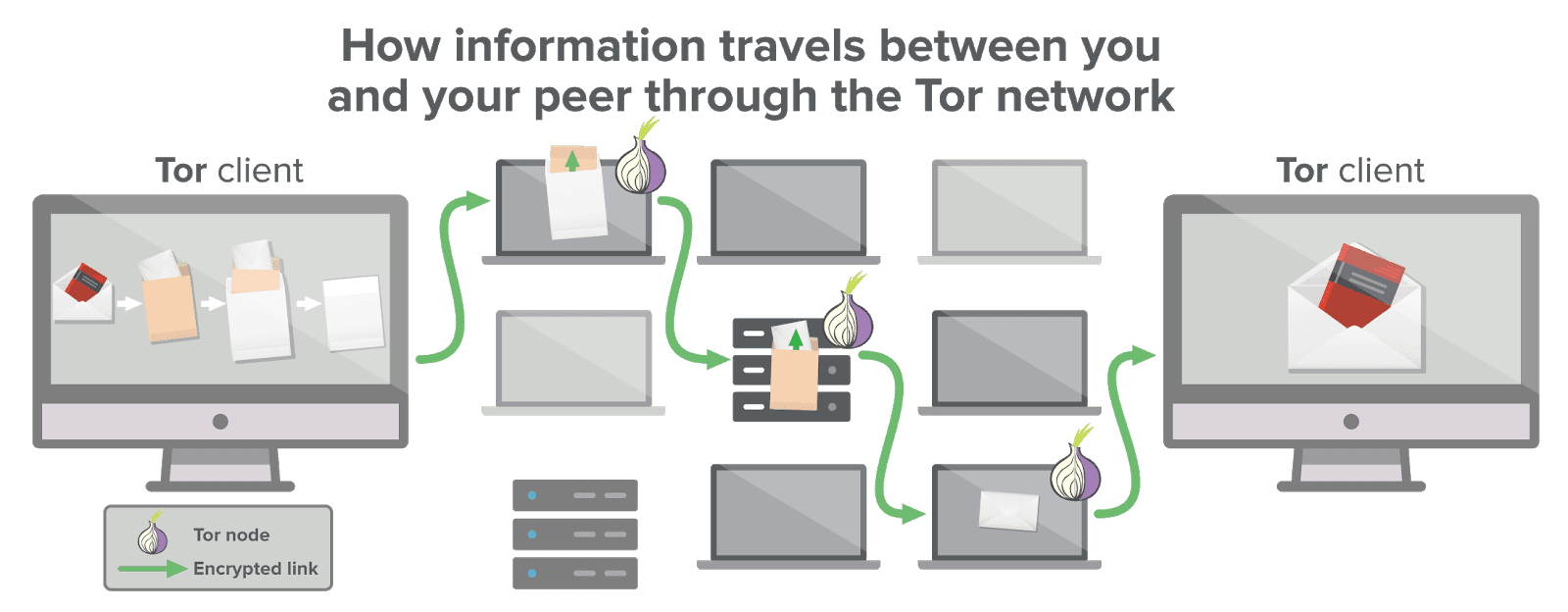
The name “TOR” was originally used as an acronym for what was called the “The Onion Routing” project in direct reference to the technology on which it is based. The free technology is designed for TCP connections and allows the anonymous use of web browsers, instant messaging, IRC, SSH, email, and P2P.
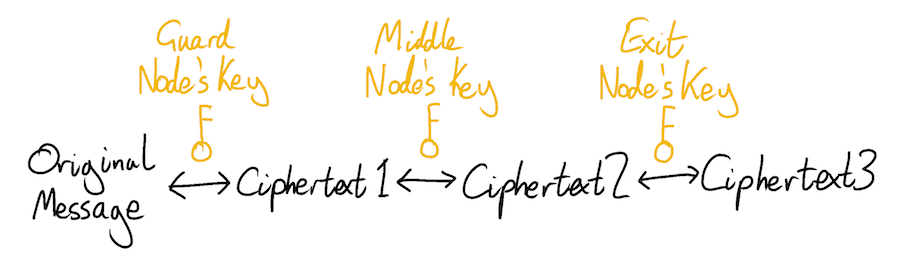
The Tor network allows users to anonymously access content on the internet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
